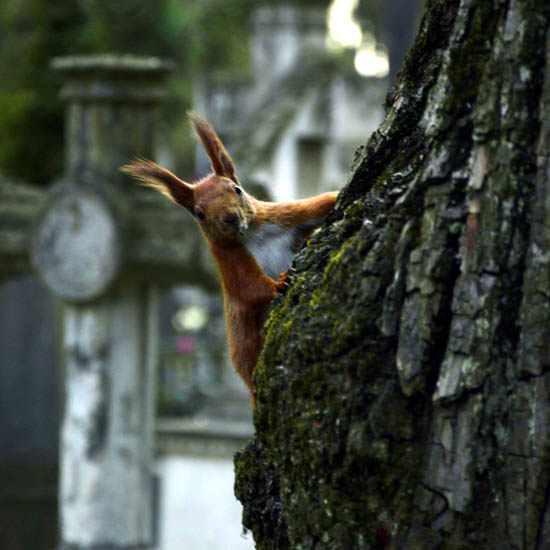
Lemberg, Gas Lamp Café in the Armenian Renaissance house, where in 1853 a Pole and a Hungarian invented kerosene. The four floors of the café are decorated with photos, newspaper clippings, shares and objects of use in the fin-de-siècle oil fields of Galicia. In the glass-enclosed top floor with open views over the rooftops of old Lemberg, a typical red-painted Soviet-era wall board with red fire buckets and shovel. “Do you know why the bottom of the fire bucket was pointed in those days?” asks András. “So it would not be stolen. Because like this, it could not be used for anything else.”
Leópolis, Café Luz de Gas en la casa renacentista armenia donde en 1853 un polaco y un húngaro inventaron el queroseno. Los cuatro pisos de la cafetería están decorados con fotos, recortes de periódico, cacharros variopintos y objetos de uso cotidiano en los campos petroleros del fin de siglo en Galizia. En la planta superior acristalada que mira sobre los tejados de la antigua Leópolis cuelga de la pared un tablero pintado de rojo, típico de la era soviética, con cubos de incendio también rojos y una pala. «¿Por qué se harían estos cubos en forma de cono en aquella época?», se pregunta András. «Así nadie se los llevaba. Con esta forma no podían utilizarse para otra cosa».
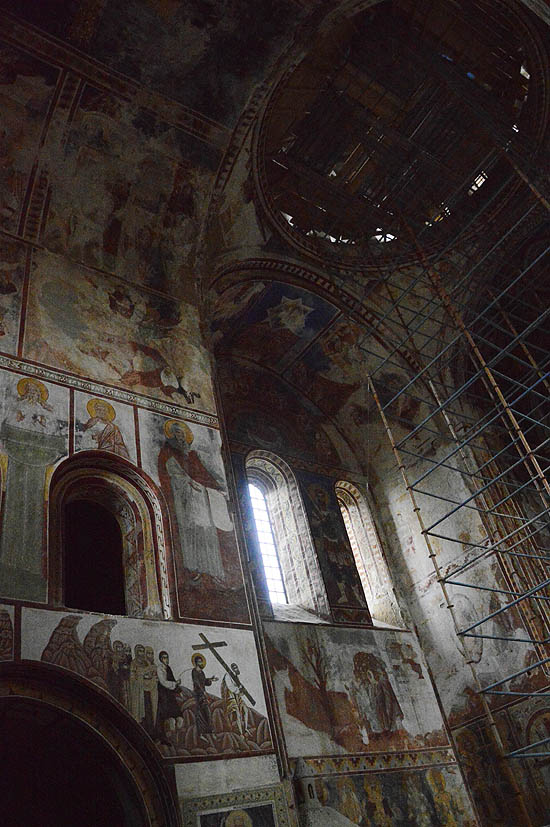
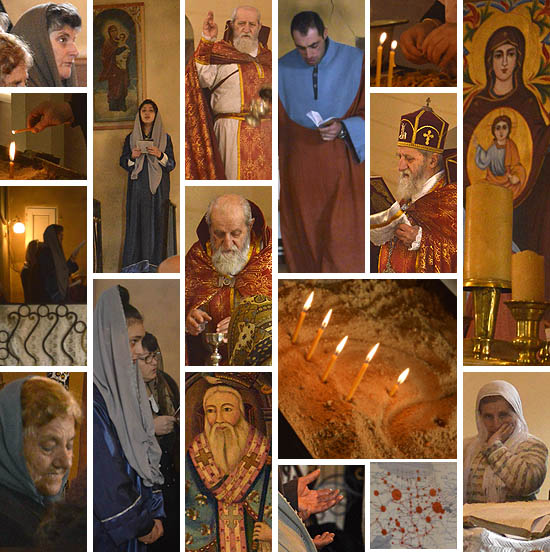
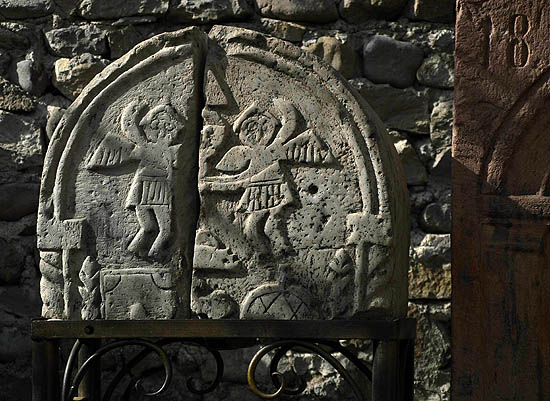
 Kutaisi, Georgia, inner courtyard of the city museum, with old Georgian grape treading tub • Kutaisi, Georgia, patio interior del museo de la ciudad con una antigua artesa para pisar la uva
Kutaisi, Georgia, inner courtyard of the city museum, with old Georgian grape treading tub • Kutaisi, Georgia, patio interior del museo de la ciudad con una antigua artesa para pisar la uva